School Wide Positive Behaviours
School-wide positive behaviour support (SWPBS) framework
School-wide positive behaviour support (SWPBS) is a framework that brings together school communities to develop positive, safe, supportive learning cultures.
SWPBS assists schools to improve social, emotional, behavioural and academic outcomes for children and young people.
When SWPBS is implemented well, teachers and students have more time to focus on relationships and classroom instruction. Students and staff benefit from:
- increased respectful and positive behaviour
- increased time focused on instruction
- improved social-emotional wellbeing
- positive and respectful relationships among students and staff
- increased adoption of evidence-based instructional practices
- a predictable learning environment with improved perceptions of safety and increased attendance
SWPBS can be implemented in any school setting to support students from Foundation through to Year 12. The framework supports schools to identify and successfully implement evidence-based whole-school practices to enhance learning outcomes for children and young people.
Key features of SWPBS
Implementation of SWPBS requires commitment by the whole school community, particularly from the principal and leadership group. All SWPBS schools implement eight essential features. They will:
- Establish a common philosophy and purpose: Staff and students use a common language to discuss behaviour. School philosophy emphasises the need to teach appropriate behaviour much like academic learning.
- Establish leadership and school-wide support: School leaders publicly endorse and support SWPBS. A team at the school leads implementation by creating, reviewing and monitoring an action plan. The work is done in collaboration by the whole staff with input from parents, students and the community.
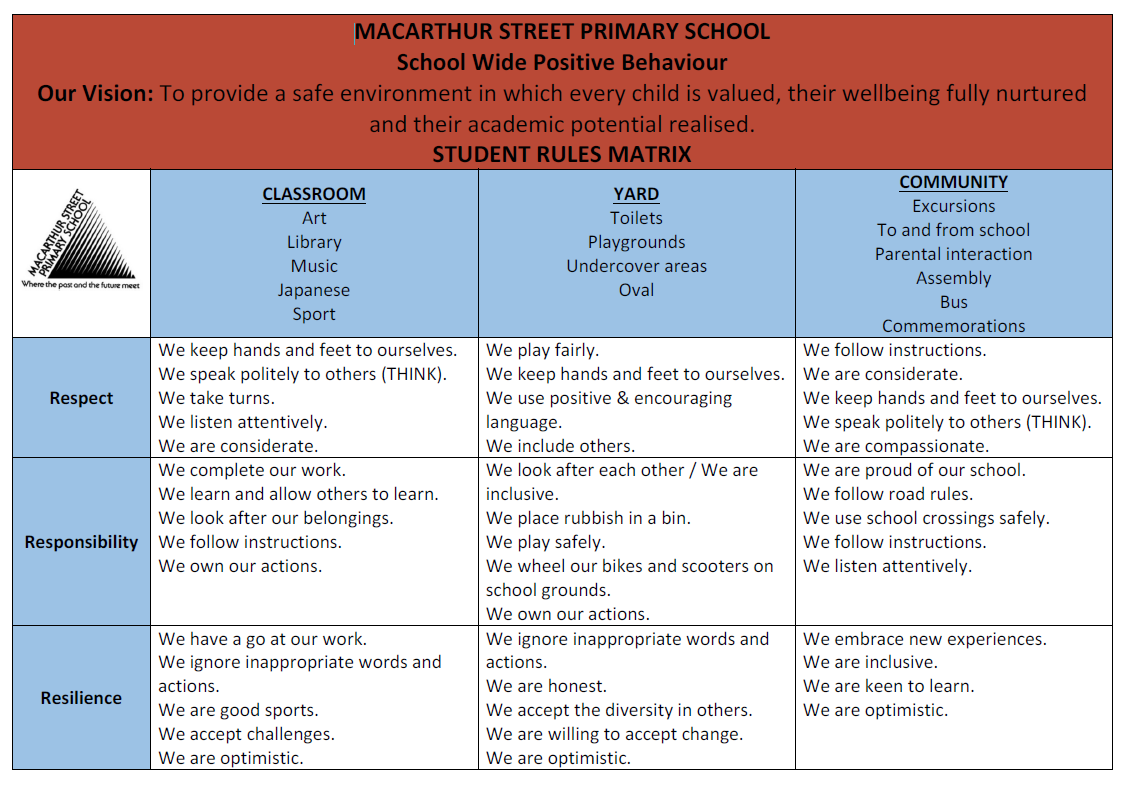
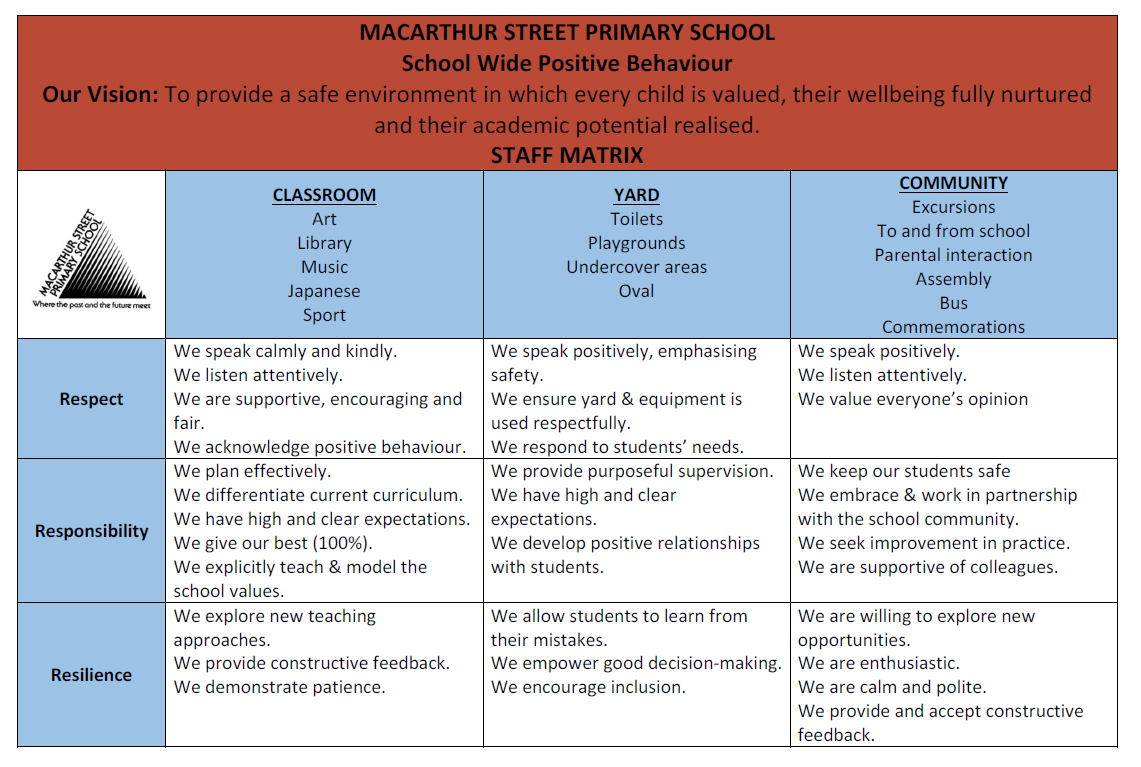
- Clearly define a set of expected behaviours: The school identifies 3 to 5 behavioural expectations that apply at all times. Clear, positively stated examples are identified and displayed in different school settings.
- Establish procedures for teaching and practising expected behaviours: A school-wide plan is developed to ensure behavioural expectations are taught to all students by all staff.
- Implement a continuum of procedures to encourage expected behaviours: School-wide systems are developed to acknowledge expected behaviour and promote commitment from all members of the school community.
- Develop a continuum of procedures to discourage inappropriate behaviour: Schools clearly define problem behaviours and identify specific strategies and responses to minor and major behavioural infractions.
- Use procedures for record-keeping, decision making and ongoing monitoring: Schools review data on repeated behaviour issues, the settings in which they occur, and the consequences most likely to be applied for inappropriate behaviours. They correlate these with other sources of data such as academic progress, and analyse this data to make necessary adjustments to school operations in an effort to reduce inappropriate behaviour.
- Support staff to use effective classroom practices: Schools establish systems to support staff to adopt evidence-based instructional practices associated with reductions in inappropriate behaviour.